interkriti®
YOUR GATEWAY TO CRETE
|
Crete
List Grid Map
Found
156
- Showing :
121 - 140
 Gournes, Iraklion at 23.9km (E) A modern competitive organisation, IMBBC (part of the Hellenic Centre for Marine Research - www.hcmr.gr) is widely recognized as one of the leading institutes in the Mediterranean. Its installations are located at Gournes, near Heraklion, Crete, where its laboratories, administration, library and conference facilities cover 1.500 m2. It has a wide range of state-of-the-art facilities needed to carry out its basic and applied research.  by Richard Ellis at 24km (W) This is my log of the E4 long distance walk along the spine of Crete from East to West - it is intended to be a useful resource for others who are contemplating a similar walk along the E4 in Crete; it is not intended in any way to be a complete route guide.
 Iraklion north at 24.3km (NE) Dia (GR: Δία & Ντία) is an uninhabited island approximately 7 nautical miles north of Heraklion. It is surrounded by small rocky inlets and its maximum length is 5kms while its maximum width 3kms. Dia is one of NATURA's protected areas due to its status as a biotope for endemic plants and for plants with low dispersal within the Southern Aegean. Image Library
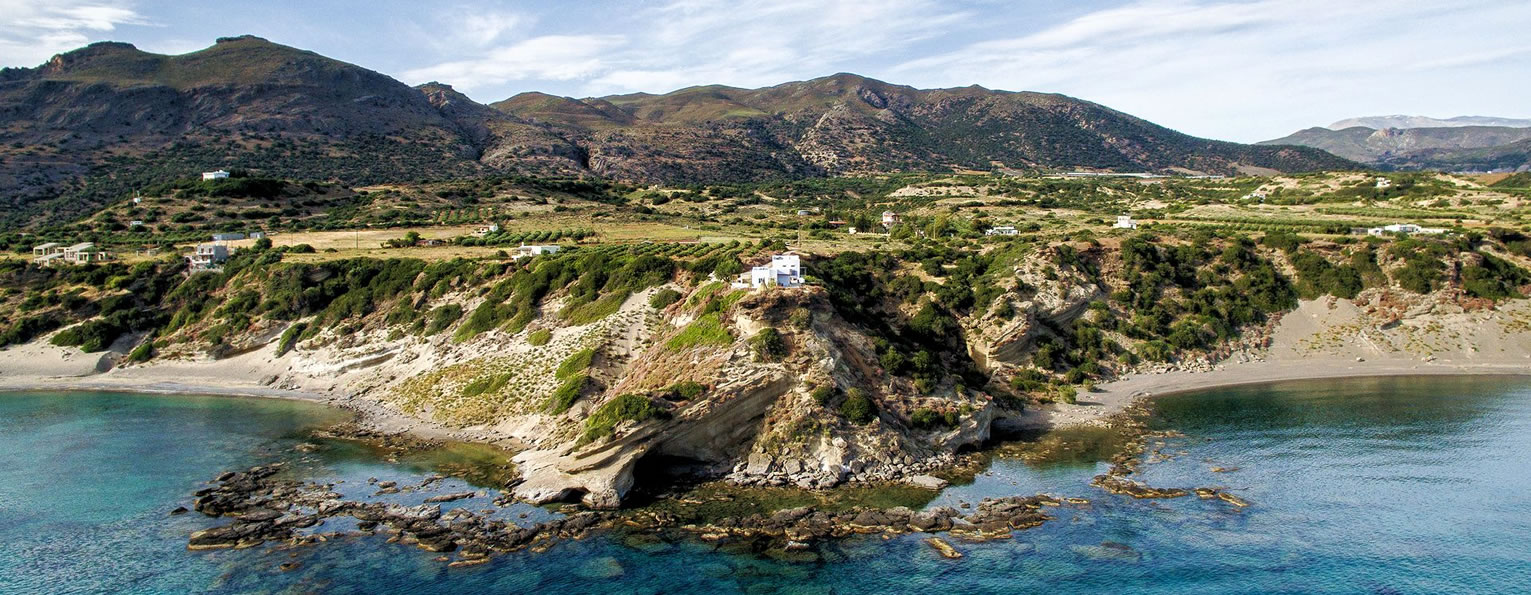
 Rethymnon North coast at 25km (NW) Bali is a small fishing village, about 40 km west of Iraklion and 37km east of Rethymno easily accessed from the international road. It has a small picturesque harbour and lots of small coves with wonderful clear beaches. Recent years Bali has been developed to a popular tourist resort but it is still preserves its traditional character. Ideal place for family holidays, with small hotels and lovely taverns serving fresh fish and local specialties.  The Venetians called the place "Atali", from its ancient name which was "Astali", while its current name was given by the Ottomans. There is also the Atali Monastery nearby, which retains the medieval name of the place and is dedicated to Saint John. The monastery is built on a small elevated peninsula overlooking the bay and the Cretan sea. Image Library
 Skotino,Gouves, Iraklion at 25.1km (E) This is one of the three largest caves in the prefecture of Heraklion. It lies at half an hour distance to the north-west from the village of Skotino and is at a height of 225 m. above sea-level. The entrance to the cave is impressive: a large arch, 27 m wide and 10 m high. To the right one can see the ruins of an ancient chapel on which the modern chapel dedicated to Aghia Paraskevi was built. There is a feast held in front of the chapel on July 26th .
 Gouves, Iraklion at 25.3km (E) Vorou (or Voritsi) lies at a height of 230 m. above sea-level and counted 62 inhabitants in 1981 and 48 in 2001. It is 25 kms away from Heraklion. To get there, you follow the National Road to Aghios Nikolaos and at kms 17.7 turn right, taking the road Gouves-Skotino- Vorou. Nowadays it is known as Voritsi but this name is not official. The name Vorou, on the other hand, in the district of Pediados is mentioned by Barozzi in 1577. At the beginning of this century there lived a wise man and a healer in the village of Voritsi. His name was Giorgos Konstantoulakis and people flocked from all over to Crete to seek his advice.
 Voritsi, Gouves at 25.9km (E) Kyra Eleoússa (GR: Κυρά Ελεούσα) Monastery is located close to the village Voroú or Voritsi. Due to its historical value the monastery and the outside area which covers 1000m has acquired protected status. Kyra Eleoussa is built according to feudal architectural style, and despite some interventions over the years it maintains many original architectural features. It is first referred in a document dating from 1606. At first it belonged to the monastery of Agia Ekaterini of Sinai but later it became part of Agarathos monastery.  Gouves, Iraklion at 26km (E) At a height of 140m. above sea-level, this village has 142 inhabitants and is 22.5 kms away from Iraklion. According to the villagers, the name comes from the church of Aghios Nikolaos Skotino at the entrance of a cave. It was built at the end of the Venetian period. Today an extra wing has been added, dedicated to Aghios Charalambos. This church of Aghios Nikolaos Skotino presumably functioned as a "Hedge School" (or "Hidden School") under Turkish rule when education had been banned. When the locals said: "We are going to Skotino (which also means "darkness")", they meant they were going to school. Turkish administration refers to this place as Skotino Perasma in 1671. Very close to the village (1.5 km) the cave of Aghia Paraskevi draws crowds of tourists and is well worth a visit.  Gouves Beach, North - East Iraklion at 26.2km (E) Káto Goúves (GR: Κάτω Γούβες or simply Gouves) is a modern tourist resort with a complete tourist infrastructure to meet all demands. Organised beaches, large modern hotels, family apartments, restaurants, small tavernas, recreation centres, sports centre, shops, car and motorbikes for rent, small ports (marinas) for small boats, in a word Kato Gouves provides everything the visitors require to spend an agreeable and carefree holiday, enjoying the sunshine by day and the thrilling night-life in the numerous bars in the area. Just a few kilometers inland there are picturesque traditional villages, historic monasteries, caves and other natural beauties. Image Library
 Gouves, Iraklion at 26.5km (E) Pano Gouves (GR: Πάνω Γούβες) is a village of the district of Pediada in the prefecture of Iraklion at a height of 100 metres above sea-level. It lies twenty kms away from Iraklion, to the right at 17.3 kms on the National Road to Aghios Nikolaos. The village is built on the western flanks of the Ederi hill (322 m.). The name comes from "edera" which means ivy and symbolises affection. The name Gouves, on the other hand, comes from Gouva and means a hollow in the earth. It also means, in Crete, a hole in which during the middle ages, people stored their wheat. The earliest reference we have of the village is that of "Guves" in 1387 documents of the Duke’s archives in Chandax. Later on, in 1577, Fr. Barozzi mentions "Guvos" in the district of Pediados, and then "Guves" in the 1583 Register, with 252 inhabitants. Finally, in 1630, Vassilikata refers to "Vuves’. This is the birthplace of the poet Ioannis Konstantinidis. There are several outstanding churches in the village, among them: Zoodochos Pigis, Aghios Giorgos, Aghios Ioannis and Panayia (dedicated to the birth of Our Lady).  Pediada, Iraklion at 26.6km (E) Apostoloi (GR: Αποστόλοι) is a village in the area of Kasteli, 360 m above sea level. It has about 490 inhabitants, and is located on the 32 km of the road leading to Kasteli in the NW part of Apostolianos Kampos, among vineyards and olive groves. Until recently tannery was a main activity among the villagers. The earliest reference to the name is to be found in a contract drawn in 1279, where Sancti Apostoli et Sophoro were lands belonging to the Venetian lord Leonardus Gradonicus, who gave them and leased them to Petro Quinino. There is another mention of the name in a document dated to 1378. It is also quoted by Fr. Barozzi in 1577 as forming part of the Pediada district. The name of the village finds its origins in the name of an old church dedicated to the Saint Apostles. The present church was built on the same site in the 19th century, in 1876. The church of Agios Giorgos is Byzantine and has wall paintings. According to village tradition, on the night of Easter in 1841, the Turks caught the Cretan leader of the revolution for the Eastern part of the island, Giorgos Vassilakis, or Vassilakogiorgi and hanged him from a fig tree.The village kapheneions serve particularly good raki and on June 29th there is a great feast in the honour of the Saint Apostles, Peter and Paul.  Pediada, Iraklion at 26.6km (E) The village of Smári (GR: Σμάρι) is a traditional Cretan village, only 10 km away from Kasteli and has 375 inhabitants. In it you will find beautiful old stone houses that have been restored, picturesque little alleys, ruins of older buildings and pottery workshops where you can purchase copies of Byzantine and Minoan ceramics. There are also some interesting churches with wonderful frescoes like the one dedicated to Sotir Christos, the Koimisi tis Panagias and Agios Giorgos. The earliest reference to the village of Smari dates back to 1375. There is a lively Cretan feast on July 20th in honour of Profitis Ilias, with much rejoicing, singing and dancing.  Gortyn archaeological site at 26.8km (S) The main acropolis of Gortyna was located on Agios Ioannis hill, to the northwest of the Agora. Acropolis can be accessed from its west side driving through Ambelouzos village to the direction of Gergeri. At a spot around 1.6 kms from Gortyna parking there is a footpath (not clearly signposted and maintained) that leads to the top of the hill. Once at the top you'll be rewarded by the magnificent view to the whole area and the archaeological site itself. The site was first inhabited in the Neolithic era and again at the end of Minoan times (1200 BC). Since then it was continuously inhabited until the Middle Byzantine period. From the first settlement only parts of walls, floors and hearths were preserved. In the 10th century BC a Geometric settlement was established fortified by a polygonal wall with towers at the corners. At the end of the 7th c. A.D., a small tripartite temple, dedicated to Athena Poliouchos was founded at the south side of the hill. From this temple some very important architectural sculptures were excavated. During the Early Byzantine period (5 - 6th century AD), a basilica was erected over the ruins of the geometric/archaic temple and, in the time of the emperor Heraclios (7th century A.D.) the last fortification with a castle in the center was built which still survives but in a very poor condition. Image Library
 Gortyn archaeological site at 26.9km (S) According to the myth, Zeus, disguised as a bull, coupled with Europe, whom he had brought from Phoenicia, under a deep- shaded plane tree on the banks of the Lethaios River. The offspring of this union were three sons, Minos, Sarpidon and Radamanthis. Later, the oldest Agora of the city of Gortyn, the Ekklesisterion (Congress hall), and the Roman Odeum were founded on this site. The plane tree was blessed and has remained ever green since that time. As his place of birth, the city was founded by King Minos himelf. According to the myth, it was on the fields of Gortyn that the bull given as a gift to Minos by Poseidon coupled with the Queen Pasiphae and out of this union Minotaur was born. Image Library
 Gortyn archaeological site at 27km (S) The Roman Odeum at Gortyn is considered one of the best and the most important of its type on Crete. Is has been founded at the North part of the Ancient Agora of the City. This semicircular building consists of three main parts: a. The Cavea, connected with a domed corridor through three wide staircases; b. the Orchestra, which has an internal diameter 8,5 m. and was paved with white and blue marble slabs; c. The Scene, which had two entrances and the paraskenion, with mosaic pavement in geometric pattern. Statues of Muses stood in the niches. Initially the building was a circular Ekklesiasterion founded in the 5th c. BC. In the portico of this public building the Great Inscription with the Law Code of Gortyn dated to the early 5th c., stood. It was destroyed twice: in the 1st century BC, and again in 46 AD. After this last destruction it was reconstructed as an Odeum. The great Inscription is considered to be the largest Greek inscription, the Queen of all Inscriptions. Its first fragments were found by the French travelers and were bought by the Louvre Museum. The most part of the Inscription was found accidentally by local farmers in 1884 and was further explored F. Halbherr. It is a Law Code inscribed in the boustrophedon system of writing. It dates in the 1st half of the 5th c. BC and is the oldest Greek and European Law Code. It consists of twelve Deltoi and was built in the Ekklesiasterion of the 5th c BC. In this Code older laws, regarding the personal and family rights of the citizens of Gortyn, were codified. Image Library
 Gortyn archaeological site at 27km (S) The oldest theater of Gortyna was on the south slope of the Profitis Ilias hill (Acropolis), opposite to the Odeum. Its cavea was partly cut into the rock and partly built. Its scene was built at the west side of the large court of the Agora, which covered the river Lethaios with a flat bridge. This scene, which H. Belli saw in the 16th c AD, was 120 m long and was already destroyed in 19th c. AD. On the proscenium there was an inscription of Julia Augusta and it was decorated with statues and relies, among which there was the statue of Europe on the Bull, with broken legs and head.This statue, as described by Admiral Spratt, is now kept in the British Museum and is dated to the 2nd c BC.  Messara, Iraklion South at 27.1km (S) Located in the valley of Messara, Gortys or Gortyn (GR: Γόρτυς or Γόρτυνα) is a must visit for all visitors to Crete. It was inhabited during Bronze Age times, but its rise to glory came almost a millennium after the downfall of the 'Minoans'. Gortyn was a prosperous city from around the middle of the 5th century BC through to the early 9th century AD, when it was finally destroyed by the Saracens (824AD), never to be rebuilt.
Image Library
 Gortyn archaeological site at 27.1km (S) Saint Titus church at Gortyn bears the name of the Apostle Titus, attendant of Apostle Paul, who was appointed as the first Christian bishop of Crete. It is one of the most important Byzantine monuments in Crete. The name was given to the ruined church by the excavators in the beginning of the 20th c., as they considered it to be the site of the saint’s martyrdom. After the discovery of the new Great Early Byzantine Basilica, just outside the village Mitropolis, its excavators have proposed that as the original bishopric basilica, as it is a century earlier than this, which in the local tradition is named and celebrated after Virgin Mary, “Kera”. The church has the plan of a three aisled inscribed cross with a low vault. It has been built of ashlar limestone. It has a narthex to the west and five entrances three of which form the trivelum with two columns. There were pillars instead of columns. Its architectural features date its foundation in the 2nd half of the 6th c. AD. Image Library
 Messara, Iraklion South at 27.2km (S) Agioi Déka (GR: Αγιοι Δέκα) is a town with 820 inhabitants in the plain of Messara, 170m above sea level, 43 km from Heraklion town and very close to the archaeological site of Gortyna. Its people are occupied mostly in agriculture - vines and olive trees. In the area there is is the oldest olive grove in Crete. The town is built on the ruins of the ancient town of Gortyn where the Holy Ten Martyrs have been martyred.  Gortyn archaeological site at 27.2km (S) The sanctuary of the Egyptian deities (1st-2nd centuries A.D.) is the only one, in the whole island, which is dedicated to the Egyptian gods Isis, Serapis and Anubis - Hermes although it is known that those gods are worshiped in other cities. The sanctuary consists of quadrilateral nave, arcade on the west, underground crypt in the south and a cistern outside east of nave. In the central alcove stood the statue of Serapis and the side statues of Isis and Hermes - Anubis. In the southern part of the temple was oblong space, underground crypt purification and a small cictern. The final construction phase of the temple dates to the 1st / 2nd century. AD, in accordance with dedicatory inscription. Image Library
|
||
|
| ||
C
O
N
T
E
N
T
S
O
N
T
E
N
T
S